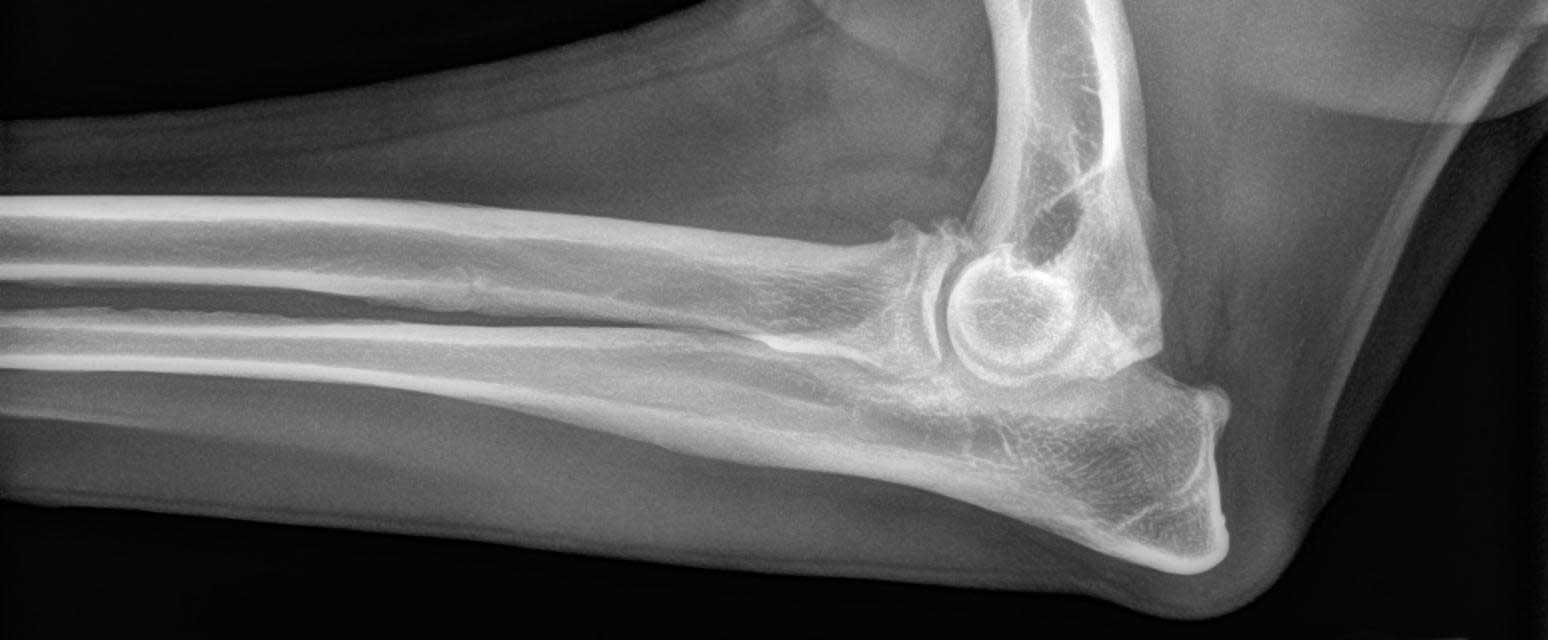
Elbow dysplasia is the term used to describe a developmental abnormality in the elbow joint which involves a complex structure of three bones. If the three bones do not fit together (articulate) absolutely perfectly the consequence is an abnormal concentration of forces on a specific region of the elbow joint causing lameness.
There are multiple management options for elbow dysplasia; conservative and surgical however rehabilitation, in either case, can facilitate mobility.
Conservative management of elbow dysplasia
Physiotherapy can help to alleviate the symptoms of elbow dysplasia and enhance your dog’s general wellbeing.
Aims of rehabilitation
- Reduce pain and swelling
- Maintain and/or increase joint mobility with a specific stretching programme which will be tailored to your dog
- Maintain and/or increase muscle mass
Physiotherapy treatment options
- Manual therapy techniques such as massage, mobilisations and stretches
- Electrotherapy such as laser, electromuscular stimulation or extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT)
- Land-based exercises for strengthening
Hydrotherapy options
Water-based therapy is a perfect environment for a dog with elbow dysplasia. The warm, supportive medium provides pain relief and allows mobilisation of joints in a buoyant / semi-buoyant environment, maintenance and strengthening of specific muscle groups and enhancement of general cardiovascular fitness which on land might not be so easy.
Hydrotherapy can be provided in a 100% buoyant environment such as our pool or in a variable buoyancy environment such as our underwater treadmill. Your chartered physiotherapist will advise you which is best for your dog depending on the severity of clinical signs and whether your dog is having conservative or post-operative rehabilitation.
What can I do to help my pet at home?
A specific home care exercise programme and walking advice will be given to you by your chartered physiotherapist and it will be uniquely designed to suit your dog’s needs. Your physiotherapist will also be able to offer advice on ADL (activities of daily living) such as how best to assist your dog in and out of a car, the avoidance of slippery floors, the avoidance of high impact activities such as jumping up or down from furniture, running up and down stairs.
The following table outlines an example elbow dysplasia rehabilitation plan:*
| Timescale | Physiotherapy aims | Physiotherapy treatment options |
| 0-2 weeks | Reduce swelling and pain |
|
| Reduce muscular guarding and maintain soft tissue flexibility |
| |
| Allow limb loading as able |
| |
| 2-4 weeks | Progress limb loading and gait re-education |
|
| Increase muscle mass |
| |
| Maintain soft tissue length and flexibility | Passive ROM and stretches | |
| Management at home |
| |
| 4-6 weeks | Continue as above, include core stability exercises |
|
| Advice on maintaining controlled exercise when dog is feeling better | ||
| 6 – 12 weeks | Increase exercise tolerance | Increase exercise level, considering land and water-based options. |
| Continue to increase core stability | Home exercise programme considering land and water-based exercises | |
| 12 weeks + | Return to full function or establish deficits and advise re long-term management. | Progress to off-lead exercise and previous exercise level if appropriate. |
*Please note that rehabilitation plans should only be followed under the guidance of a qualified rehabilitation professional, who will be able to provide a tailored plan based on the individual patient’s rehabilitation needs.